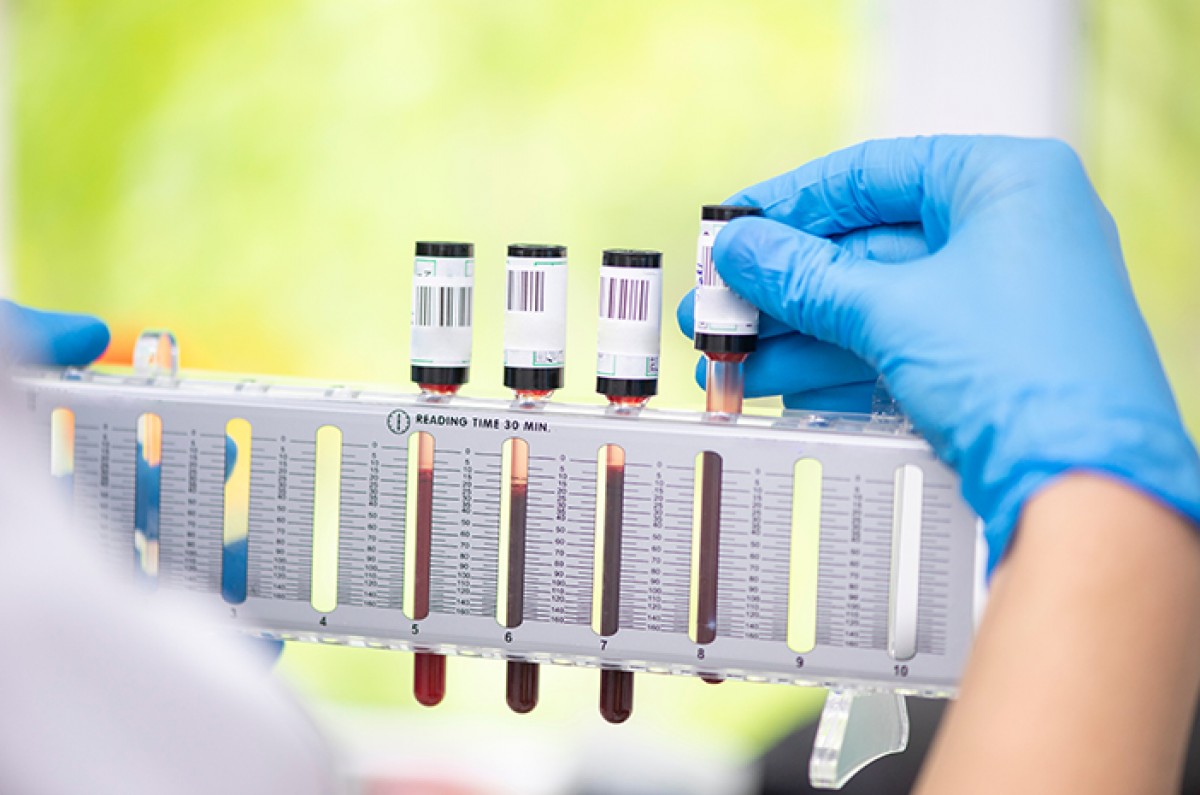
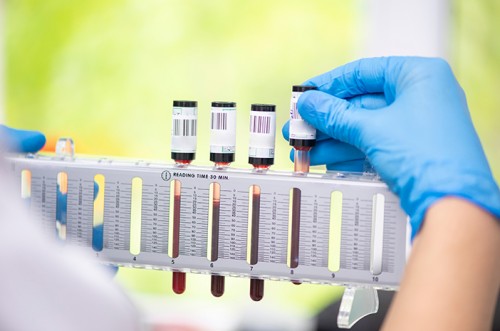
"The erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) is the most common examination method to determine indications of inflammation in the body due to blood cell clumping; however, further examination is still needed to determine the type of infection that is occurring."
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) measures how quickly red blood cells in a blood sample settle at the bottom of a test tube over a specified period. The rate of blood sedimentation is influenced by the structure of the blood cells. When an infection occurs, blood cells tend to clump together, which causes them to settle more quickly because of their increased mass. The presence of these clumps in the blood serves as an indicator of inflammation or infection in the body.
 Figure 1. Blood clots due to infection in the blood vessels
Figure 1. Blood clots due to infection in the blood vessels
Currently, the ESR, particularly the Westergren method, is recognized as the gold standard by the International Committee for Standardization in Hematology (ICSH) and the Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). This method is widely used for the initial diagnosis of specific diseases due to its affordability and ease of execution by medical professionals and analysts.
The ESR test serves several important functions:
- Detection of Inflammation: ESR is used to detect and confirm inflammation in the body. When inflammation occurs, proteins in the blood can alter the sedimentation rate, which provides clues to the presence of an inflammatory condition.
- Diagnosis and Monitoring of Diseases: The ESR test is often conducted alongside other tests to diagnose diseases associated with inflammation, such as autoimmune diseases, infections, or other inflammatory conditions.
- Evaluation of Treatment Response: During the treatment of diseases involving inflammation, ESR is used as a monitoring tool to assess how well the body responds to treatment. Changes in ESR results can help doctors evaluate the effectiveness of treatment.
- Identifying Unknown Causes of Fever: The ESR test can help in identifying unclear or undiagnosed causes of fever by indicating the presence of inflammatory processes in the body.
- Detection of Arthritis and Other Symptoms: The ESR test is also useful in identifying certain types of arthritis and other symptoms affecting the muscles, aiding in the diagnosis and monitoring of these conditions.
The normal ESR range for adult men (under 50 years old) is approximately 0-15 millimeters per hour (mm/hour), and for adult women (under 50 years old) it is around 0-20 mm/hour. ESR test results must be assessed by a doctor in conjunction with clinical symptoms and other tests to make an accurate diagnosis. Extremely high ESR values (>100 mm/hour) may indicate chronic infections, lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma, heart disease, local brain inflammation, arthritis, or melanoma skin cancer.
The Seasight Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) Tube 0-150mm and 0-170mm
The Seasight Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) Tube 0-150mm and 0-170mm is specifically designed for measuring the ESR using the Westergren method, which is recognized as the gold standard by the International Council for Standardization in Hematology (ICSH). Available in two variants, 0-150mm and 0-170mm, these tubes have the following key features:
- Polypropylene USP VI Material: Made from high-quality, durable polypropylene that resists breakage or cracking and withstands temperature changes. The material also maintains minimal discoloration, ensuring long-term usability and stability.
- Clear Reading Scale: Both the 0-150mm and 0-170mm tubes are equipped with a clear, easy-to-read scale that allows users to obtain ESR results easily and precisely, enhancing measurement accuracy and consistency.
- Long Shelf Life (2 Years): With a shelf life of up to two years, The Seasight Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) Tube 0-150mm and 0-170mm Tubes ensure long-term effectiveness and reliability, minimizing laboratory waste.
- 3.8% Sodium Citrate Solution (0.2 ml): Each tube contains 0.2 ml of 3.8% sodium citrate anticoagulant solution, which prevents blood clotting during testing, ensuring accurate ESR measurements. Available in packs of 100 pieces, this offers a cost-effective solution for high-volume testing.
The Seasight Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) Tube 0-150mm and 0-170mm are ideal for hematology laboratories that require fast, accurate results while adhering to international standards.
Doctors commonly recommend an ESR test for patients exhibiting the following symptoms:
- Fever and joint pain
- Pain in the shoulders, neck, or hips
- Sudden and significant weight loss
- Digestive issues, such as blood in the stool
Reference:
- Kevin Tishkowski, National Center for Biotechnology Information. (2023). Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate
- International Committee for Standardization in Haematology (ICSH). (2011). ICSH recommendations for modified and alternate methods measuring the erythrocyte sedimentation rate
- US National Library of Medicine. (2022). ESR (erythrocyte sedimentation rate)