HIV is a Sexually Transmitted Infection (STI) caused by a virus that attacks the immune system. Treatment can control the infection and prevent disease progression and being diagnosed early means you can start therapy right away. Check out this article to find out 3 types of medical examinations for HIV detection.
HIV (Human Immunodeficiency Virus) is an infectious disease caused by a virus that attacks the immune system. By damaging your immune system, HIV interferes with your body's ability to fight infection and disease. If HIV is not treated, it can lead to AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome).
HIV is a Sexually Transmitted Infection (STI). It can also be spread by contact with infected blood and from illicit-drug injection or sharing needles. It can also be spread from mother to child during pregnancy, childbirth or breastfeeding. Without medication, it may take years before HIV weakens your immune system to the point that you have AIDS.
If you are a person at high risk of contracting or transmitting this disease, it is best to have a medical examination or HIV test as early as possible. Testing for HIV is the only way to know for sure if you have HIV or not. Many people do not have any symptoms and can live for many years without knowing they have the virus.
Medications can control the infection and prevent progression of the disease. Being diagnosed early means you can start treatment, which will help you live a long and healthy life. Getting tested for HIV is quick, easy, painless and confidential.
The following are 3 types of medical examinations for HIV detection:
- Antibody Test
An antibody test is a medical examination that is carried out by checking the content of HIV antibodies in the blood. Antibodies against HIV will be produced by the body's immune system when a person has been infected with the HIV virus and can only be detected 1 to 3 months after the patient has been infected with the HIV virus.
Several types of antibody tests to detect HIV/AIDS infection are:
-
- Rapid test: carried out by dropping a patient's blood/serum/plasma sample onto a testing cassette. This test is quick, it only takes 10-20 minutes to read the results
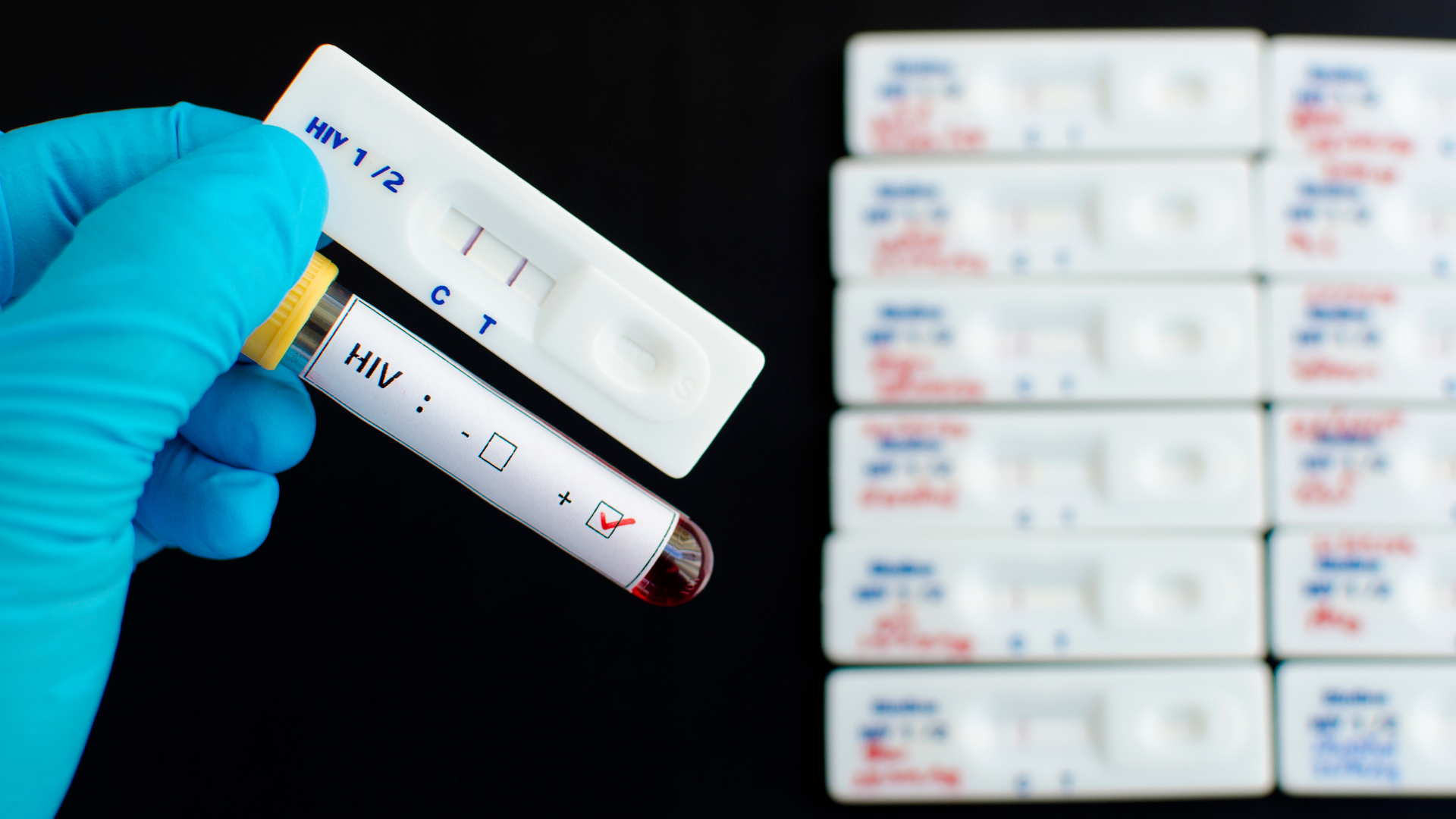

Picture 1. Rapid test
-
- ELISA test: carried out by placing a sample of the patient's blood into a special tube. Then, the blood sample will be analyzed in the laboratory to see if it contains HIV antibodies. This test usually takes 1-3 days
Picture 2. ELISA test
-
- Western Blot test: is a follow-up test from the ELISA test. More precisely, a western blot test is performed to confirm the specific binding of the antibody to the HIV protein
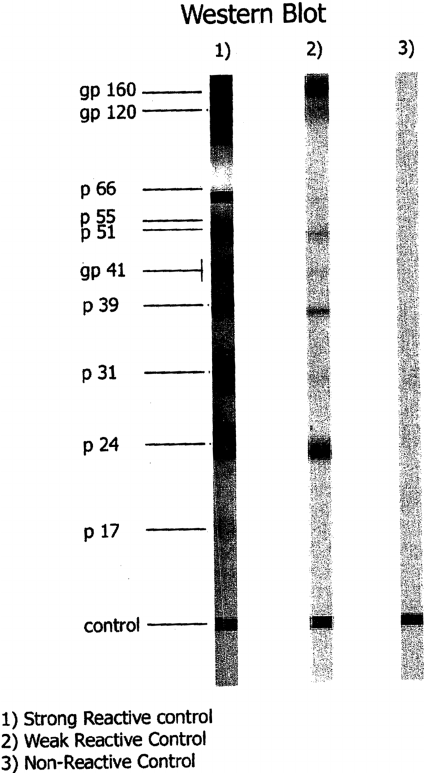
Picture 3. Western Blot Test
- Antibody-Antigen Test
Antibody-antigen test or Ab-Ag test is a combination of tests performed to detect the p24 protein (HIV antigen) and HIV-1 or HIV-2 antibodies in the patient's blood.
This test is considered more accurate and can be used as an early check of HIV/AIDS because antigens will appear faster than antibodies, which is around 2 to 6 weeks after infection.
- PCR test
The PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) test is an HIV test that is considered to have the highest level of accuracy. This test are used to detect HIV's genetic material, called RNA, in the patient's blood in a laboratory. The results of this test require a longer time, which is 2 days.
By knowing HIV status, you and your partner will get information to maintain health. If the examination results are positive, the doctor will provide care and treatment earlier to prevent worsening of the disease, reduce symptoms and prevent transmission to other people.
Meanwhile, if the test results are negative, then this condition makes it easier for you and your partner to decide on various matters related to sexual activity to treatments that can be done to prevent HIV.
There are various HIV prevention measures that can be taken, such as:
- Using a condom
- Choose less risky sexual behaviours
- Never sharing needles with other people
- Never sharing razors with other people
References:
- CDC. (2022). Types of HIV Tests
- HIVgov. (2020). HIV Testing Overview
- Stanford Healthcare. (2022). Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) for HIV
- Mayo Clinic. (2022). HIV/AIDS