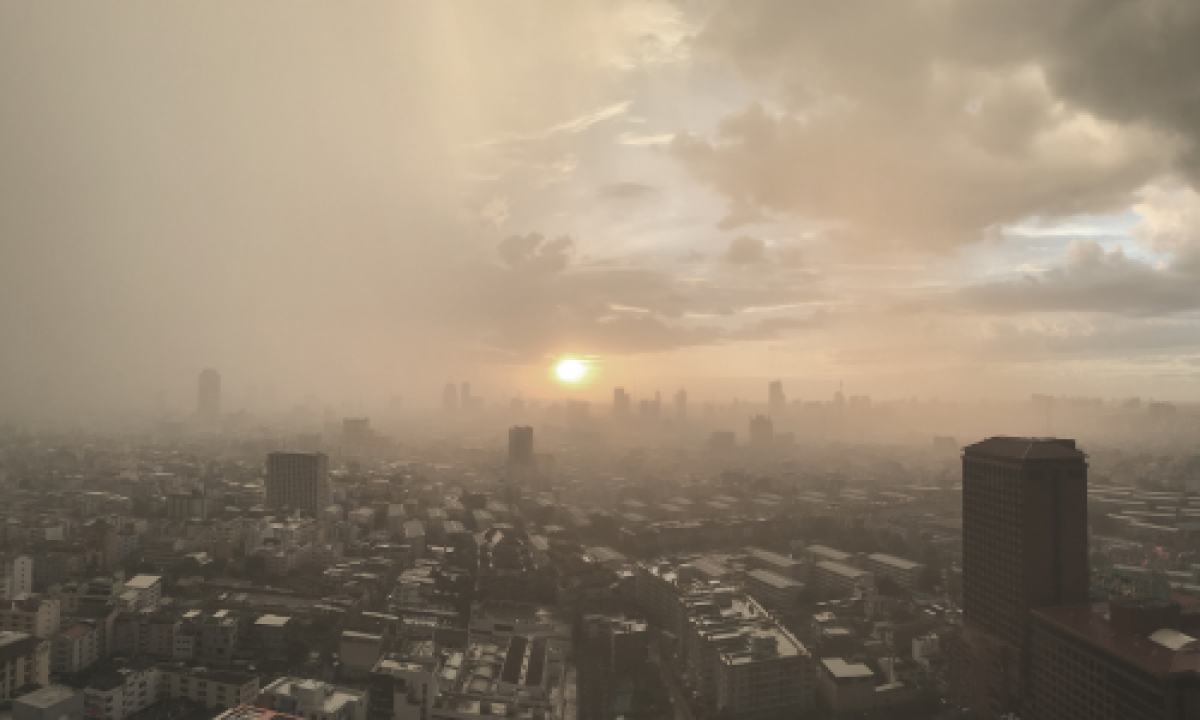
Air pollution is the greatest environmental threat to public health globally. Residential pollution, fossil fuels, transport, waste burning, chemical and mining industries are the main human-made sources of fine particles globally that pollute our air. Air pollution and climate change are closely linked as all major pollutants have an impact on the climate. Improving our air quality will bring health, development, and environmental benefits.
Air pollution is a mix of hazardous substances from both human-made and natural sources.
Vehicle emissions, fuel oils and natural gas, by-products of manufacturing and power generation, particularly coal-fueled power plants, and fumes from chemical production are the primary sources of human-made air pollution. Nature is also releasing hazardous substances into the air, such as smoke from wildfires ash and gases from volcanic eruptions and gases like methane which are emitted from decomposing organic matter in soils.
Air pollution and climate change affect each other through complex interactions in the atmosphere. Air pollution is intricately linked with climate change because both problems come largely from the same sources, such as emissions from burning fossil fuels. Both are threats to people’s health and the environment worldwide.
Exposure to high levels of air pollution can cause a variety of adverse health outcomes. It increases the risk of respiratory infections, heart disease and lung cancer. Both short- and long-term exposure to air pollutants have been associated with health impacts. More severe impacts affect people who are already ill. Children, the elderly and poor people are more susceptible. The most health-harmful pollutants – closely associated with excessive premature mortality – are fine PM2.5 particles that penetrate deep into lung passageways.
PM or particulate matter is the term for particles found in the air, including dust, dirt, soot, smoke, and liquid droplets. Large concentrations of particulate matter are typically emitted by sources such as diesel vehicles and coal-fired power plants. Particles less than 10 micrometers in diameter (PM10) pose a health concern because they can be inhaled into and accumulate in the respiratory system. Particles less than 2.5 micrometers in diameter (PM2.5) are referred to as "fine" particles and pose the greatest health risks.
Air pollution exposure is associated with oxidative stress and inflammation in human cells, which may lay a foundation for chronic diseases and cancer. In 2013, the International Agency for Research on Cancer of the World Health Organization (IARC WHO) classified air pollution as a human carcinogen.
Some diseases caused by air pollution:
- Lung Cancer
Particles in air pollution can cause lung cancer, about 6% of deaths worldwide related to outdoor air pollution are due to lung cancer.
- Asthma Attacks
Some pollution like smoke, carbon monoxide, tiny particles like those in dust or smoke can get stuck in lungs. This kind of pollution can damage lungs and cause someone with asthma to have more attacks.
- Chronic Bronchitis
Someone who lived in a city and regularly breathe in traffic fumes may have chronic (long lasting) bronchitis. This can be caused by exhaust from cars, trucks, and other vehicles pollutes the air.
- COPD
Chronic bronchitis and emphysema are common conditions that lead to Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD). These conditions block air flow in the lungs. Long-term exposure to gases, particles, or smoke is the main cause. Studies have shown that COPD is more common in areas where air pollution is high.
- Pneumonia
Nitrogen oxide and sulfur dioxide in air pollution boost chances of pneumonia, or lung inflammation. Children and the elderly are especially at risk. Pneumonia is the leading cause of childhood death worldwide. Older adults are especially likely to spend time in a hospital for pneumonia after long-term exposure to air pollution.
- Heart Disease
Air pollution can lead to a higher risk of heart attack, irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia), heart failure, and stroke. Tiny particles in the pollution are small enough to travel to the blood vessels and cause inflammation. Over time, they can make heart disease set in faster. People who live near busy streets or factories run a greater risk.
- Premature Birth
Exposure to air pollution is linked to preterm, or premature, birth. Pollution can raise the level of toxic chemicals in the blood. This stresses a pregnant woman’s immune system. This can weaken the placenta and cause an early birth. This can lead to health problems for the baby right away or in the long term. Air pollution also may cause low birth weight.
- Learning and Memory Problems
Studies have shown that air pollution can have a harmful effect on the brain. Traffic-related air pollution can slow a baby’s brain and behavior development. In the elderly, it raises the chances of dementia.
Fighting air pollution is everybody’s responsibility. We all need to do more, a lot more. Swiftly and proactively to reduce air pollution. Concerted and coordinated efforts with active involvement of all the sectors is imperative. This includes the Government (national, state and local governments), cities, community at large and individuals.
References:
- National Institute of Environmental Health Sciences. (2023). Air Pollution and Your Health
- United Nations Environment Programe. (2022). Pollution Action Note – Data you need to know
- WebMD. (2021). Health Effects of Air Pollution
- World Health Organization. (2019). Health consequences of air pollution on populations