Diabetes mellitus is a chronic metabolic disorder characterized by the body's inability to produce or effectively use insulin, leading to elevated blood glucose (sugar) levels. If left uncontrolled, diabetes can cause severe complications such as kidney failure, blindness, slow-healing wounds, heart attacks, and strokes.
According to the International Diabetes Federation (IDF) Diabetes Atlas 2021, Indonesia ranks 5th in the world with over 19.5 million people living with diabetes, more than 50% of whom are unaware they have the disease. This underscores the critical need for early detection and regular blood glucose monitoring to prevent fatal complications.
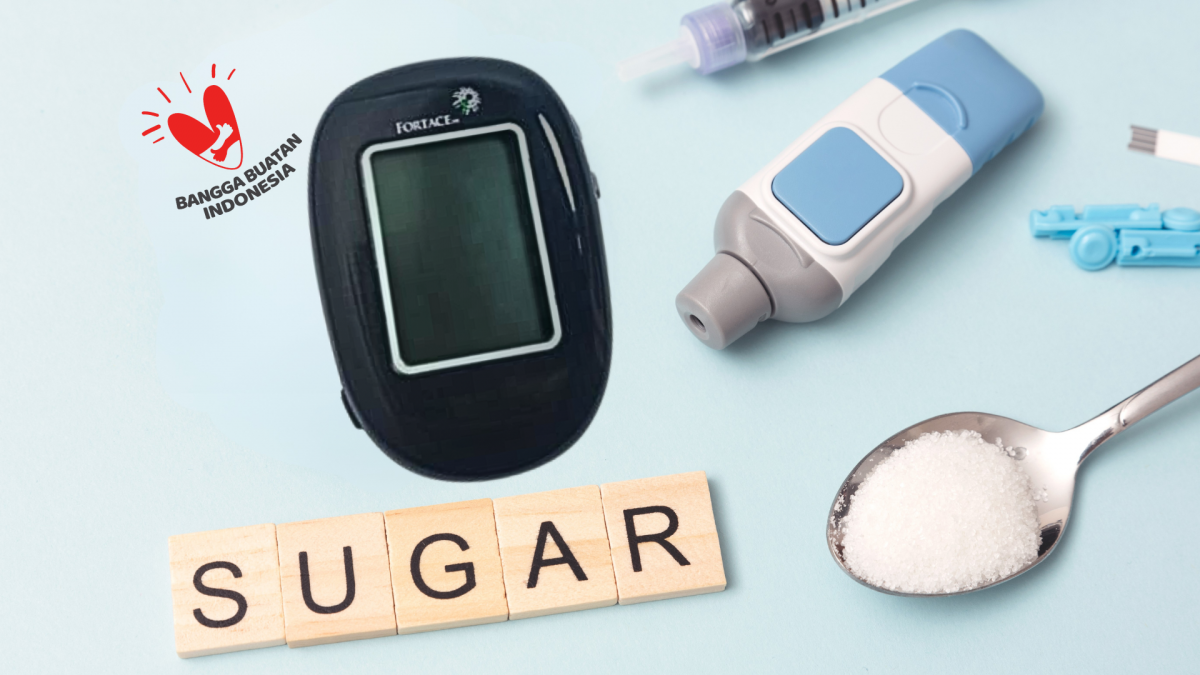
The Role of Blood Glucose Meters in Diabetes Management
Blood glucose meters, or glucometers, play a vital role in diabetes care by:
-
Early Screening: Helping detect prediabetes or type 2 diabetes before symptoms worsen.
-
Self-Monitoring: Allowing patients to check and maintain stable blood glucose levels regularly.
-
Treatment Evaluation: Assisting healthcare professionals in adjusting medications, diet, and lifestyle plans based on accurate glucose readings.
Regular use of glucometers has been proven to reduce the risk of diabetes-related complications and improve patients’ quality of life.
Key Features of Indonesia’s Domestic Blood Glucose Meter
The locally developed blood glucose meter supports fresh capillary whole blood samples with a measurement range from 1.1 to 33.3 mmol/L. It provides results in mmol/L or mg/dL units, requires only 0.5 µL of blood per test, and has a battery life supporting up to 1000 tests using a CR2032 battery. Other features include date and time display, alternate site testing, PC connectivity, and automatic shutdown after 100 seconds of inactivity. The test strips have a validity period of 24 months, and the device functions optimally within temperatures of 10-40°C and humidity between 10%-90%.
This innovation represents a major step in making affordable, reliable diabetes monitoring tools widely accessible in Indonesia.
Understanding Diabetes: Symptoms and Risks of Poor Monitoring
Common Symptoms of Diabetes
People with diabetes often experience symptoms such as:
-
Frequent urination
-
Excessive thirst
-
Unexplained weight loss
-
Extreme hunger
-
Fatigue and weakness
-
Blurred vision
-
Slow-healing wounds
-
Tingling or numbness in hands and feet
If these symptoms are present, prompt blood glucose testing is essential.
Complications from Poorly Controlled Diabetes
Without regular monitoring and management, high blood glucose levels can cause serious complications, including:
-
Kidney damage (nephropathy): Leading to kidney failure requiring dialysis or transplant.
-
Eye problems (retinopathy): Causing vision loss or blindness.
-
Poor wound healing: Increasing risk of infections and amputations.
-
Cardiovascular diseases, Such as heart attacks and strokes, are leading causes of death among diabetics.
-
Nerve damage (neuropathy) results in pain, numbness, and loss of sensation.
These risks highlight why regular blood sugar checks using accurate and user-friendly devices are indispensable in diabetes care.
References:
-
International Diabetes Federation. (2021). IDF Diabetes Atlas (10th ed.). Retrieved from https://diabetesatlas.org
-
Indonesian Ministry of Health. (2022). Situation and Analysis of Diabetes Mellitus in Indonesia. Jakarta: Center for Data and Information, Ministry of Health.
Link: https://pusdatin.kemkes.go.id -
American Diabetes Association. (2023). Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2023. Diabetes Care, 46(Suppl.1), S1–S291.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.2337/dc23-S001 -
Indonesian Society of Endocrinology (PERKENI). (2021). Consensus on the Management and Prevention of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus in Indonesia.
Link: https://pbperkeni.or.id -
National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK). (2023). Diabetes Complications. Retrieved from https://www.niddk.nih.gov/health-information/diabetes/overview/preventing-problems
- Mayo Clinic. (2024). Diabetes: Symptoms and Causes. Retrieved from https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/diabetes