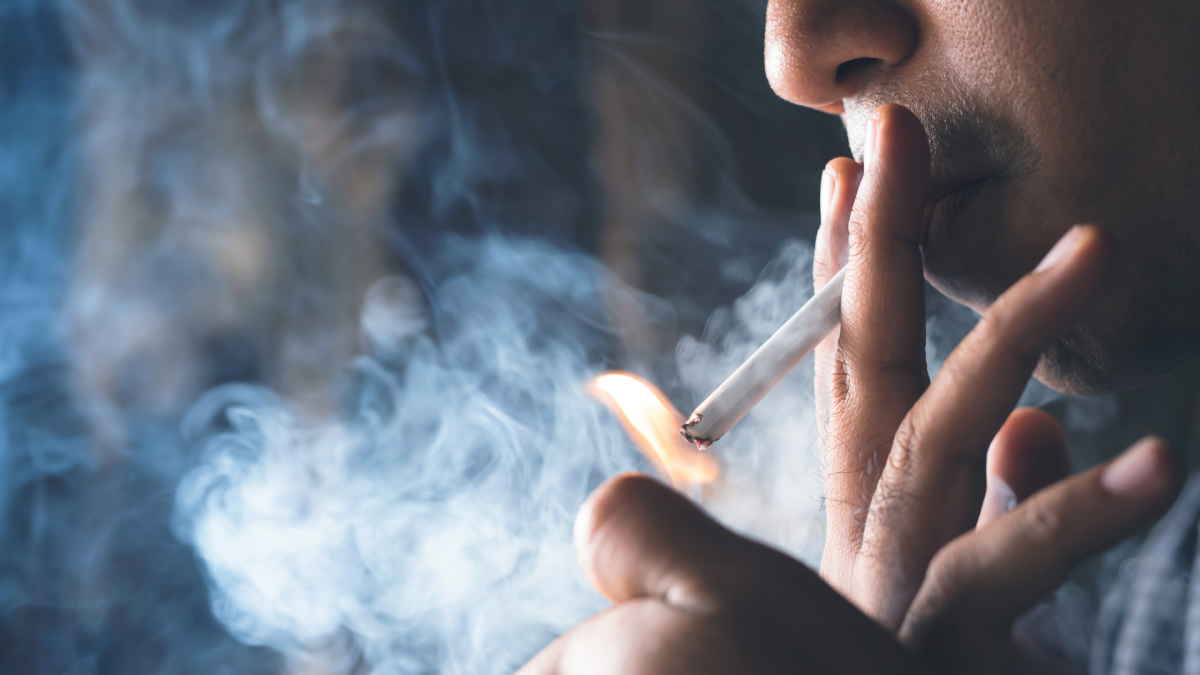
Smoking is the number one risk factor for lung cancer. More than 7000 chemicals contained in cigarettes and their smoke have the potential to damage lung cells in various ways. Not only active smokers who have a high risk, but passive smokers are also at risk.
Cigarette smoke can be a major cause of lung cancer. Smoking habits or exposure to cigarette smoke directly increases the risk of lung cancer.
When a person inhales cigarette smoke, thousands of these chemicals will enter the lungs. Cigarette smoke contains a toxic mixture of more than 7000 chemicals, about 70 of which are carcinogenic (cancer-causing) substances. Examples of carcinogenic materials include; arsenic, benzene, cadmium, chromium, formaldehyde, N-nitrosamine, nickel, and vinyl chloride. These chemicals have the potential to damage lung cells.
Here are some ways the chemicals in cigarette smoke can cause lung cancer:
- Damage the DNA of Lung Cells
When exposed to carcinogens, DNA strands begin to break. The cells will multiply excessively and prevent apoptosis (programmed cell death that provides room for replacement with new, healthy cells). These changes will cause cancer cells to multiply uncontrollably and almost can not die.
- Disrupts Cell Repair Process
Damaged DNA usually can be repaired and mutated cells can be destroyed by mechanisms that help the body fight cancer. Tumor suppressor genes code for enzymes that trigger the death of damaged cells and instruct the body to make new, healthy cells.
However, chromium from cigarette smoke can bind to DNA and effectively silence tumor suppressor genes. Arsenic and nickel could also do the same thing by driving mutations in tumor suppressor genes.
- Causes Inflammation
When inhaled cigarette smoke, body will release pro-inflammatory compounds to minimize damage to cells. Over time, the inflammation that occurs can damage the cell's DNA and change the way cells stick to one another. This allows cancer cells to migrate freely and become invasive.
- Causes Damage to Cilia
Cilia are tiny hair-like structures that line the airways that remove waste from the lungs. Toxins in cigarette smoke, such as formaldehyde, can paralyze and damage the cilia. This will cause the harmful particles in cigarette smoke to stay in the lungs longer.
- Disrupt the Immune System
Although the carcinogens in cigarette smoke are involved in the formation of cancerous tumors, other chemicals can contribute to the development of lung cancer by suppressing the overall immune system. Both nicotine and tar can impair the body's innate immune response and block several cancer-preventing mechanisms, such as apoptosis.
People who are at high risk of developing lung cancer are not only active smokers, but people who are often exposed to secondhand smoke are also at risk for lung cancer. Especially in pregnant women and children.
It's never too late to stop. The longer you smoke, the higher your risk of developing lung cancer. When this smoking habit is stopped, the body can repair much of the damage caused by the chemicals in cigarette smoke. When you stop smoking, it’s not only yourself who will get the benefits, but so will the people around you.
References:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. (2022). What Are the Risk Factors for Lung Cancer?
- Mayo Clinic. (2022). Lung Cancer
- (2021). The Connection Between Smoking and Lung Cancer