31 January 2025
WHY LBC PROVIDES MORE REPRESENTATIVE RESULTS IN CERVICAL CANCER SCREENING
Cervical cancer screening is a crucial step in the early detection of cervical cancer, one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths among women worldwide. One increasingly popular method for this screening is Liquid-Based Cytology (LBC). LBC offers several advantages over conventional methods, such as the Pap smear, by providing more representative and accurate results.

20 November 2024
HPV DNA TESTING USING URINE SAMPLES: A NON-INVASIVE SCREENING FOR CERVICAL CANCER
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is the leading cause of cervical cancer, a disease that remains one of the top causes of death among women worldwide. Conventional methods like Pap smears have been the standard for screening, but limitations in accessibility and comfort often reduce participation. Urine-based HPV DNA testing is now emerging as an innovative alternative, offering a non-invasive, comfortable, accurate approach that can be applied to a broader population.
06 September 2024
IMPORTANT! MEN ALSO NEED HPV DNA SCREENING
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is a common virus that can infect the skin and mucous membranes of the body, such as the mouth, throat, cervix, and genital areas. While many people are aware of HPV risks in women, especially related to cervical cancer, there is still a lack of awareness about its impact on men. HPV can also lead to various cancers in men, including penile, anal, and oropharyngeal (mouth and throat) cancers.

14 August 2024
NEW CERVICAL CANCER SCREENING METHOD: REDUCING THE NEED FOR INVASIVE PROCEDURES
“Our study, for the first time, demonstrates that analyzing mucus samples can distinguish cervical tumors from normal tissues more accurately than serum samples,” said Professor Takuma Fujii from Fujita Health University who led the research team. “Using such a method as an additional option to traditional screening techniques could help discover cancer and precancerous conditions at an earlier stage"...
02 August 2024
HPV DNA TESTING: ESSENTIAL INSIGHTS AND BENEFITS
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is a virus that spreads through sexual contact and is a leading cause of cervical cancer. HPV DNA testing is an essential tool for the early detection of HPV infection and assessing the risk of cervical cancer. This article provides an in-depth explanation of HPV DNA testing, including its basic principles, procedures, benefits, and implications.

07 April 2024
HEALTHY COMMUNITIES, HEALTHY WORLD: HEALTH TRANSFORMATION ON WORLD HEALTH DAY
Every year, World Health Day is commemorated as a significant moment to highlight the global challenges faced in efforts to create healthier communities. With the theme "Healthy Communities, Healthy World," World Health Day emphasizes the importance of cross-sector collaboration to achieve inclusive and sustainable health transformation.
16 February 2024
EMPOWERING WOMEN: FACING CERVICAL CANCER WITH KNOWLEDGE AND ACTION
Cervical cancer is one of the most common types of cancer affecting women worldwide. However, many women still lack information about this disease, which can lead to late diagnosis and ineffective treatment. Therefore, it is crucial for every woman to empower herself with accurate information about cervical cancer and the steps that can be taken to prevent and manage this disease.

16 November 2023
SUCCESSES AND CHALLENGES IN EARLY CANCER DETECTION: UNDERSTANDING THE PROCESS AND HOPE FOR THE FUTURE
Cancer remains a significant challenge in the field of healthcare, but there is strong hope that early detection can change the game. Early cancer detection has brought significant successes in prognosis and recovery, yet there are challenges to overcome to achieve better detection rates in the future.

18 October 2023
HPV TYPES LINKED TO CERVICAL CANCER: UNDERSTANDING ADENOCARCINOMA AND ADENOSQUAMOUS CARCINOMA
Cervical cancer is one of the most common types of cancer occurring in women worldwide. This cancer is typically caused by infection with the Human Papilloma Virus (HPV). HPV is a family of DNA viruses with over 200 types that can infect humans. Some types of HPV, particularly high-risk types, can lead to cell changes that have the potential to become cancerous. In this article, we will discuss the specific types of HPV that are associated with two types of cervical cancer: adenocarcinoma and adenosquamous carcinoma.

26 September 2023
EARLY DETECTION OF OVARIAN CANCER: THE IMPORTANCE OF AWARENESS AND ROUTINE EXAMINATIONS
Ovarian cancer, a formidable adversary, often evades early detection due to its subtle symptoms. Recognizing its signs and undergoing routine screenings are pivotal in its early intervention. Detecting ovarian cancer in its nascent stages significantly improves prognosis and treatment outcomes. This article emphasizes the imperative of awareness and regular examinations in the battle against this insidious disease.

17 July 2023
MAINTAINING FAMILY HEALTH THROUGH REGULAR HEALTH CHECK-UP
Maintaining family health is crucial for achieving a quality and harmonious life. One important step to take is regularly conducting health check-ups. Periodic health check-ups help in the early detection of potential health issues before symptoms arise, allowing for early intervention. They also aid in preventing the spread of communicable diseases among family members. Furthermore, health check-ups promote awareness of healthy lifestyles and reduce long-term healthcare costs.
07 May 2023
EMPOWERING WOMEN'S HEALTH: THE SIGNIFICANCE OF CERVICAL CANCER SCREENING AND EDUCATION FROM MULTIPLE PERSPECTIVES
The article highlights the importance of early detection of cervical cancer and the roles of various parties in educating the public about the importance of regular screenings. Healthcare providers, governments, health institutions, communities, non-profit organizations, family, friends, media, and influencers all have a part to play in raising awareness and making cervical cancer screening accessible and affordable. By working together, it is hoped that public awareness of cervical cancer and the importance of regular screening will increase, leading to a reduction in the number of cases and deaths caused by cervical cancer.
04 February 2023
FINE NEEDLE ASPIRATION CYTOLOGY (FNAC)
Fine needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) entails using a narrow gauge (25-22G) needle to collect a sample of a lesion for microscopic examination. It allows a minimally invasive, rapid diagnosis of tissue but does not preserve its histological architecture.
04 January 2023
BE AWARE THYROID CANCER! WOMEN ARE MORE AT RISK
Cancer of the thyroid occurs in the butterfly-shaped gland at the base of the neck. The cause of thyroid cancer is poorly understood but may involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Some people have no symptoms. To know more about thyroid cancer, see the following article...
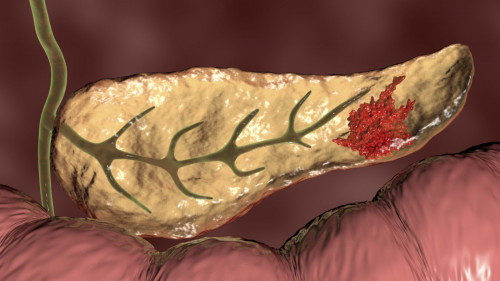
17 November 2022
THE USEFULNESS OF LIQUID-BASED CYTOLOGY FOR ENDOSCOPIC ULTRASOUND-GUIDED TISSUE ACQUISITION OF SOLID PANCREATIC MASSES
Liquid-based cytology (LBC) is used primarily for cervical cytology, although it is also used for analyzing liquid samples such as urine and ascites specimens, as well as fine needle aspiration material, such as those obtained from breast and thyroid. The usefulness of the LBC method for endoscopic ultrasound-guided tissue acquisition (EUS-TA) of solid pancreatic masses was recently reported. The LBC method can produce multiple pathological slides and can be applied to immunocytochemistry and genetic analyses. In this article, we review the usefulness of LBC for EUS-TA of solid pancreatic masses.
12 November 2022
National Health Day 2022
National Health Day is celebrated every November 12. Everyone can play a role in raising awareness of the importance of health, PT Isotekindo also plays a role in increasing health awareness by providing various types of medical devices that can be used for personal use or in health facilities.

30 June 2022
GET TO KNOW THE 3 STEPS FOR EARLY CANCER DIAGNOSIS
Early diagnosis of cancer focuses on detecting symptomatic patients as early as possible so they have the best chance for successful treatment. When cancer care is delayed or inaccessible there is a lower chance of survival, greater problems associated with treatment, and higher costs of care. Early diagnosis improves cancer outcomes by providing care at the earliest possible stage and is, therefore, an important public health strategy in all settings.

02 March 2022
LBC FOR CERVICAL PRE-CANCER SCREENING, HOW MUCH ACCURATE IS IT?
Liquid-Based cytology is a method for screening pre-cancer cytology. The development of research results and the application of technology has succeeded in developing improvements to the preparation of Pap tests, namely the LBC (Liquid Based Cytology) Pap Test method. The advantages of cytological preparation of Pap test LBC method will be explained in this article
25 February 2022
CONVENTIONAL PAP SMEAR AND LBC PAP SMEAR: WHICH IS MORE SUPERIOR?
Liquid-based cervical cytology was developed to improve the diagnostic reliability of Papanicolaou (Pap) smears. Two methods are used for cervical cytology. The first one is the conventional Papanicolaou (PAP) and the second one is liquid-based cytology (LBC). Although various studies in western countries established the role of LBC in cervical cancer screening, no large-scale study was conducted in our population to compare the two techniques for cervical cancer screeningTherefore, in this study, we compared the diagnostic utility of these two techniques for detecting cervical epithelial lesions.

21 December 2021
EARLY DETECTION OF CERVICAL PRE CANCER
Cervical cancer is one of the most common types of cancer in women. In Indonesia, cervical cancer ranks second after breast cancer as the most common type of cancer of all cancer cases in 2020. There are more than 36,000 cases and 21,000 death cause this cancer.